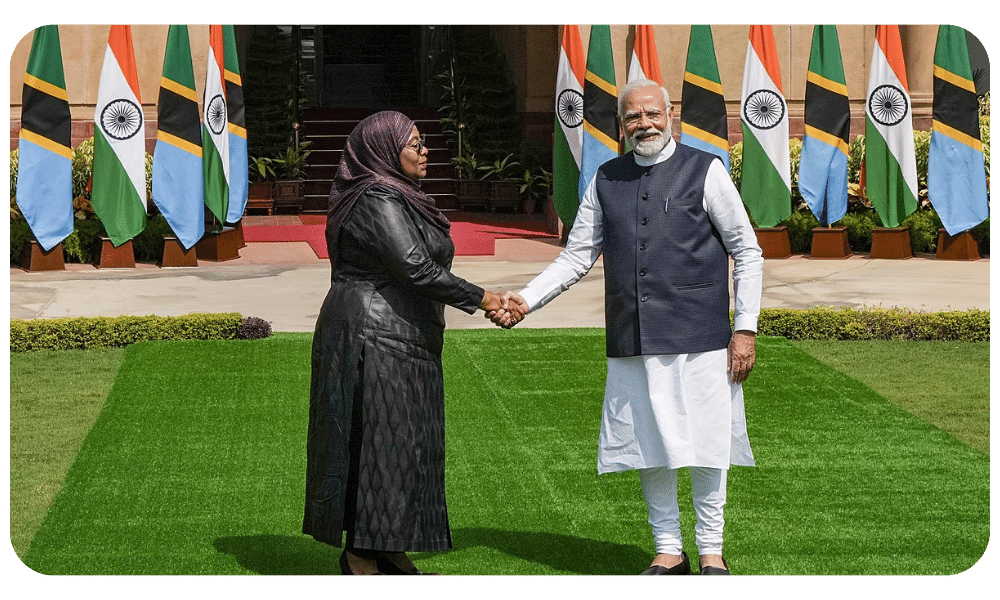
Tanzanian President Hassan first woman to receive JNU honorary doctorate
What is the news?
- Tanzanian President Samia Suluhu Hassan was conferred an honorary doctorate by Jawaharlal Nehru University on Tuesday, becoming the first woman to be bestowed with the honour of her exceptional achievements to public service and her dedication to advancing peace and prosperity in Africa, she was granted the degree.
- It also honour of her in fostering stronger India-Tanzania relations, promoting economic diplomacy, and acheiving success in regional integration and multilateralism”.
- In the history of India-Tanzania ties, President Hassan’s receipt of an honorary doctorate is a noteworthy development.
- It is an indication of India’s profound regard for President Hassan and the Tanzanian people.
Summary of the Joint Statement during the State Visit of the President of Tanzania to India and launch of Strategic Partnership between India and Tanzania (8-10 October 2023):
- President Samia Suluhu Hassan of Tanzania visited India from 8-10 October 2023, accompanied by a high-level delegation.
- She was accorded a ceremonial welcome and paid her respects to Mahatma Gandhi.
- President Samia Suluhu Hassan and Prime Minister Narendra Modi held bilateral talks and discussed various issues of mutual interest.
- The leaders emphasized the close and cooperative relations between India and Tanzania, with a focus on development cooperation.
- They highlighted the recent visits of ministers from both countries, which have strengthened bilateral relations.
- The leaders announced the elevation of the Indo-Tanzania relationship to a Strategic Partnership, focusing on areas such as Maritime Security, Defense Cooperation, Development Partnership, Trade, and Investment.
- Several Memoranda of Understanding (MoUs) were signed during the visit, covering various sectors.
- Both sides expressed satisfaction with the increasing level of bilateral political engagement and strategic dialogue, including cooperation on regional and global issues.
- They agreed to enhance defense cooperation through the Joint Defense Cooperation Committee and expanding the scope of cooperation in the defense industry.
- The leaders emphasized the importance of maritime security and agreed to enhance cooperation in the Indian Ocean region.
- Both sides expressed commitment to promoting trade and investment, exploring new areas of trade, and harmonizing trade volume data.
- They appreciated India’s development assistance in sectors such as water, health, education, capacity building, scholarships, and ICT.
- Cooperation in the fields of education, skill development, and ICT was discussed, including the establishment of vocational training centers and collaboration in space technologies.
- The leaders highlighted the significance of establishing the first overseas campus of the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT), Madras in Zanzibar.
- Both sides expressed a desire to broaden people-to-people contacts, cultural exchanges, and tourism between the two countries.
What is the relation between Tanzania and India?
- India and Tanzania share a lengthy and intimate historical history together. One of the first nations to acknowledge Tanzania’s independence in 1961 was India. There are close cultural and economic ties between the two nations.
- India is Tanzania’s biggest trading partner and its biggest investor. Tanzania is home to several Indian businesses, such as Tata, Airtel, and Mahindra & Mahindra.
- Tanzania and India are closely related culturally. Tanzania is home to a sizable population of Indian descent. In addition, the two nations have collaborated on other cultural initiatives, including the founding of the Mahatma Gandhi Centre for Cultural Studies in Dar es Salaam.
MOUs that Tanzania and India currently have:

Tanzania and India have recently inked many Memorandums of Understanding. Among the significant MOUs are:
During this visit ,India and Tanzania sign 6 MoUs:
- India and Tanzania signed six MoUs in the field of Sports, Maritime Industry, Cultural Exchange, setting up Industrial Park in Tanzania, sharing successful digital solutions implemented at population scale for digital transformation and sharing White Shipping Information.
Previous:
- MOU on Agriculture-Related Cooperation (2002)
- Memorandum of Understanding on Tourism Cooperation (2008)
- Agreement on Collaboration in the Education Sector (2016)
- Memorandum of Understanding on Defence Cooperation(2019 )
A number of real projects have come about because of these MOUs, including
- The India-Tanzania Centre of Excellence in ICT (Information and Communications Technology) was opened in Dar es Salaam.
- Launch of the Bilateral Investment Promotion and Protection Agreement between India and Tanzania.
- giving Indian scholarships to kids in Tanzania.
- Indian medical teams being sent to Tanzania.
- The two countries’ cultural teams visiting each other.
- The MOUs between India and Tanzania are a big part of making their relationship stronger and encouraging them to work together in many areas.
India and Tanzania share a lengthy and intimate historical history together. One of the first nations to acknowledge Tanzania’s independence in 1961 was India. There are close cultural and economic ties between the two nations.
Two Nations connections to the Past:
- Tanzania and India have a long-standing historical tie. Evidence of centuries-long trade and cultural exchange exists between the two locations.
- India became as Tanzania’s main labour supplier in the 1800s. Indian labourers were imported to Tanzania to work on railway construction projects and plantations.
- Tanzania was a fervent supporter of India during the Indian independence movement. Additionally, Tanzania was one of the founding members of the Non-Aligned Movement, which Yugoslavia and India also co-founded.
Present-day Relations:
- Tanzania and India currently share close cultural and economic relations. India is Tanzania’s biggest trading partner and its biggest investor. Tanzania is home to several Indian businesses, such as Tata, Airtel, and Mahindra & Mahindra.
- Tanzania and India are closely related culturally as well. Tanzania is home to a sizable population of Indian descent. In addition, the two nations have collaborated on other cultural initiatives, including the founding of the Mahatma Gandhi Centre for Cultural Studies in Dar es Salaam.
The link between Tanzania and India is significant from several angles:

First off, the partnership is a fantastic illustration of South-South collaboration. The phrase “South-South cooperation” refers to collaboration between developing nations. It is predicated on the ideas of reciprocity and independence.
Second, India’s strategic interests in Africa depend on the connection. Africa has a sizable youthful population and is a continent that is developing quickly. India has several strategic interests in Africa, including energy security, trade, and investment.
Third, the partnership is critical to India’s standing as a world leader. Tanzania and India have a close relationship, which indicates India’s increasing global influence.
In summary:
- Tanzania and India have a mutually beneficial partnership. Their collaboration has greatly benefited both nations. The partnership serves as an example of South-South collaboration.
What is South-South cooperation (SSC)?
- South-South cooperation (SSC) is a process where developing countries exchange resources, technology, and knowledge. It’s a mechanism used by countries and international organizations to foster collaboration among developing countries in the Global South.
SSC contributes to:
- National well-being
- National and collective self-reliance
- Attaining internationally agreed development goals, including the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development
SSC is a type of technology cooperation. It tries to:
- Interact and exchange knowledge, skills, and successful initiatives in a variety of fields
- Pursue individual and/or shared national capacity development objectives
- Use regional and interregional collective actions
- Examples of developed countries of the South include: India, Brazil, China, South Africa.
The theme of the 2023 United Nations Day was “Solidarity, Equity and Partnership: Unlocking South-South Cooperation to Achieve the SDGs”.
The History of Tanzania:

- Portuguese explorers first set foot on Tanzania’s coast in the fifteenth century, when they built commercial posts. Other European powers, such as the Arabs, Germans, and British, came after the Portuguese.
- German East Africa was founded in 1885, including the area that is now Tanzania. Due to the harsh and exploitative nature of German rule, the indigenous inhabitants staged several uprisings.
- Tanganyika, or the interior of Tanzania, was made a British mission following Germany’s defeat in World War I. As a protectorate, Zanzibar continued to be ruled by the British.
- Tanganyika separated from Great Britain in 1961. The inaugural president of the nation was Julius Nyerere. A socialist leader, Nyerere advocated for African socialism and independence.
- The United Republic of Tanzania was formed in 1964 by the union of Tanganyika and Zanzibar. Nyerere continued to lead the newly formed nation.
- Tanzania achieved notable advancements in healthcare, education, and the fight against poverty under Nyerere’s leadership. But the nation also had to deal with economic problems like mismanagement and corruption.
- After Nyerere retired in 1985, Ali Hassan Mwinyi took over. Mwinyi instituted several economic reforms, including as liberalisation and privatisation.
- Benjamin Mkapa was elected president in 1995. In addition to carrying out Mwinyi’s economic reforms, Mkapa made strides against corruption.
- Jakaya Kikwete won the presidency in 2005. Kikwete concentrated on enhancing the economy and infrastructure of the nation.
- John Magufuli won the presidency in 2015. Magufuli was a populist politician who prioritised building up the nation’s infrastructure and battling corruption. When he passed away in office in 2021, Samia Suluhu Hassan took over as Tanzania’s first female president.
- The historical ties between Tanzania and India are discussed in reference to Zanzibar. From 1890 until 1964, Zanzibar was a protectorate of the British. Together with Tanganyika, Zanzibar formed the United Republic of Tanzania in 1964.
- Zanzibar is now a province of Tanzania with some degree of autonomy. It has a president and government of its own. In addition to being a well-liked travel destination, Zanzibar serves as Tanzania’s main economic hub.
QuizTime:
Which of the following is the official language of Tanzania?
(a) Swahili
(b) English
(c) Arabic
(d) None of the above
Answer: (a) Swahili
Explanation: Swahili is the official language of Tanzania, along with English. Swahili is a Bantu language that is spoken by over 150 million people worldwide. It is the most widely spoken language in Africa.
Mains Question:

Discuss the significance of the historical relations between India and Tanzania. What are the key areas of cooperation between the two countries today?
Model Answer:
- India and Tanzania have been friends for a very long time. When Tanzania got its freedom in 1961, India was one of the first places to recognise it. Both the economies and cultures of the two countries are very connected.
- India is the country that invests the most in Tanzania and trades with it the most. Tata, Airtel, and Mahindra & Mahindra are some of the Indian companies that do business in Tanzania.
- There are also strong cultural ties between India and Tanzania. Ethiopia is home to a lot of people who are from India. They have also worked together on a number of artistic projects, such as building the Mahatma Gandhi Centre for artistic Studies in Dar es Salaam.
The key areas of cooperation between India and Tanzania today include:
- Trade and investment
- Agriculture
- Tourism
- Education
- Defence
- On top of that, the two countries work together on a number of regional and global problems, such as fighting terrorism and climate change.
- India and Tanzania get a lot out of their friendship with each other. It has been very helpful for both countries to work together. The relationship also shows how South-South countries can work together.
During this visit ,India and Tanzania sign 6 MoUs:
- India and Tanzania signed six MoUs in the field of Sports, Maritime Industry, Cultural Exchange, setting up Industrial Park in Tanzania, sharing successful digital solutions implemented at population scale for digital transformation and sharing White Shipping Information.







0 Comments